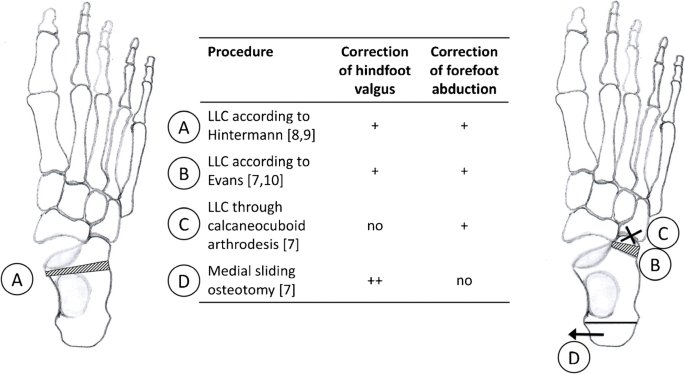
Anterior calcaneal osteotomy lateral column lengthening a lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the deformity.
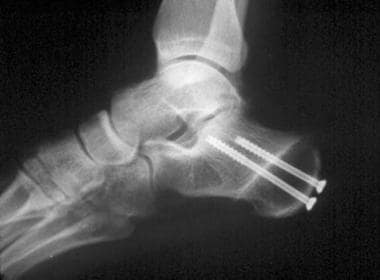
Lateral calcaneal slide osteotomy.
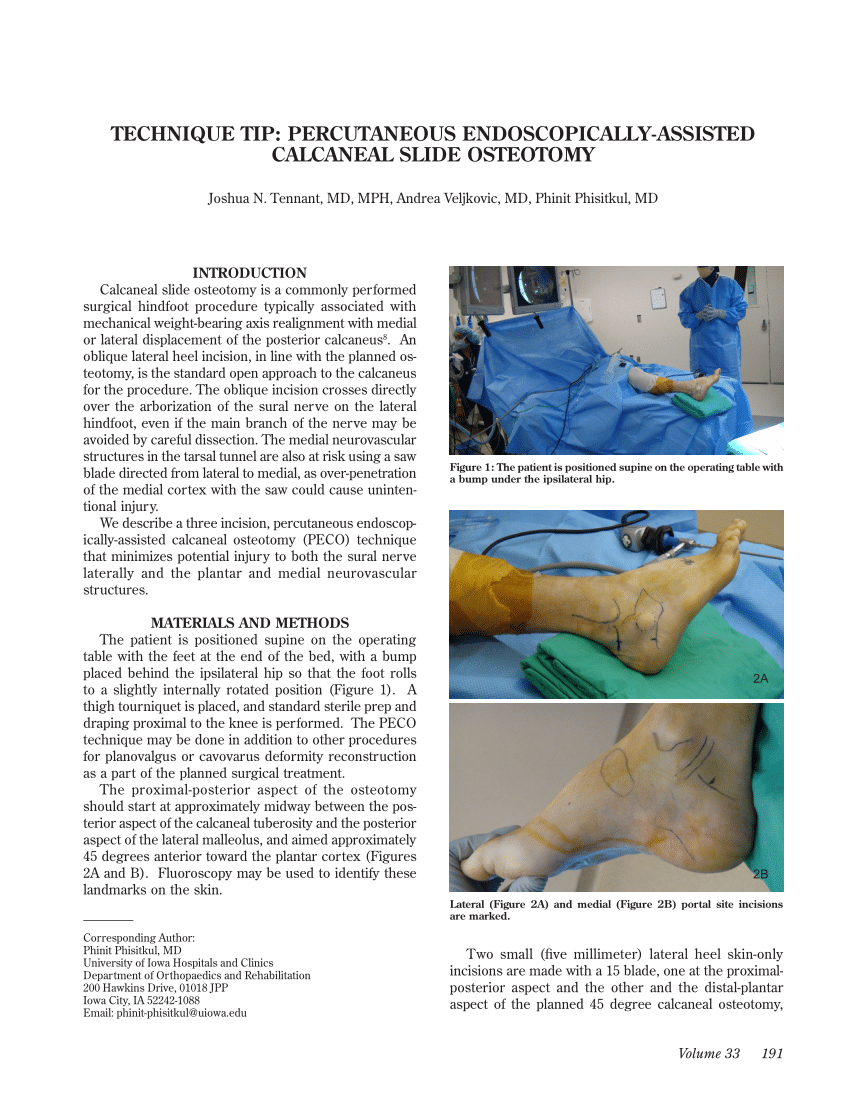
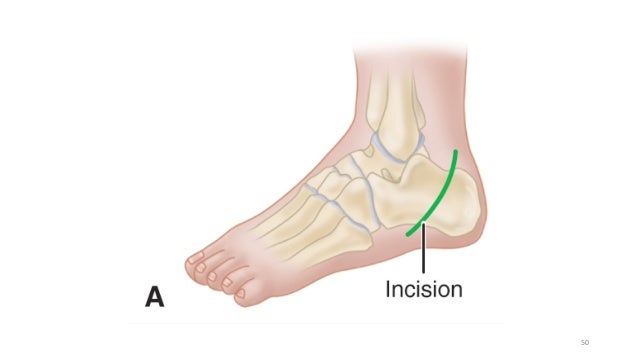
In a calcaneal osteotomy an incision is made on the outer or lateral side of the foot.
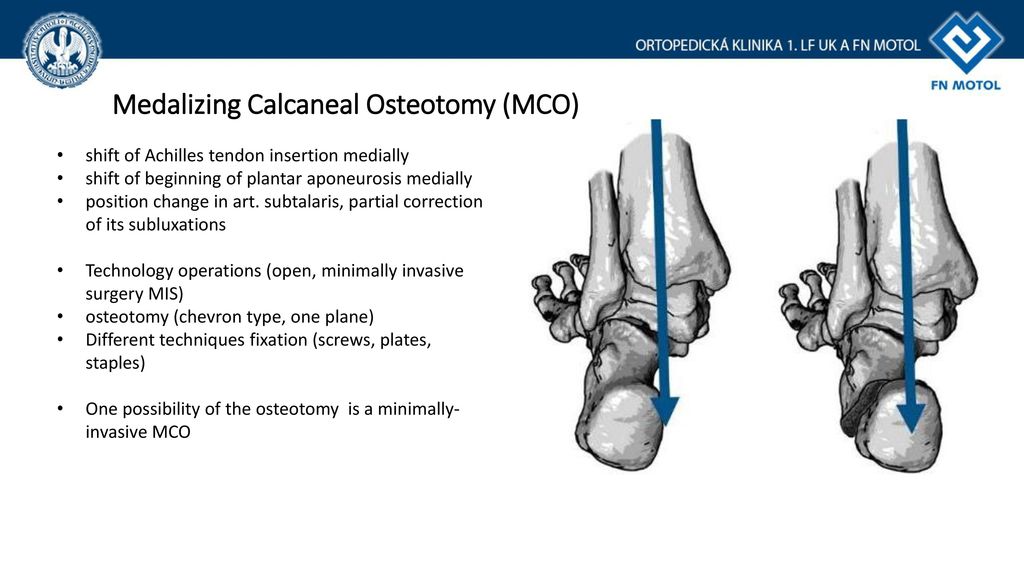
The posterior osteotomy fragment is manually mobilized and shifted laterally.
The osteotomy is stabilized with two cannulated screws followed by wound closure.
Use a sagittal saw first to score the lateral cortex and then advance the saw just prior to the medial cortex.
A variety of fixation methods exist including screws and plates.
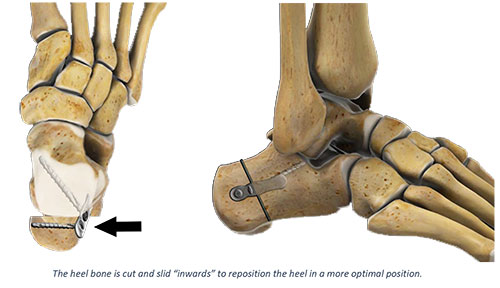
The purpose of a calcaneal osteotomy is to shift the heel bone towards the inside medial or outside lateral.
Make an osteotomy parallel to the incision ensuring that it extends anterior to the plantar calcaneal tubercle.
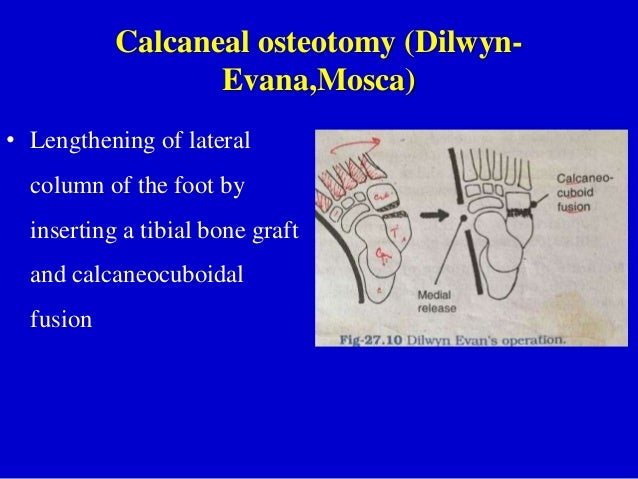
Lateral column lengthening by calcaneal osteotomy combined with soft tissue reconstruction for treatment of severe posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
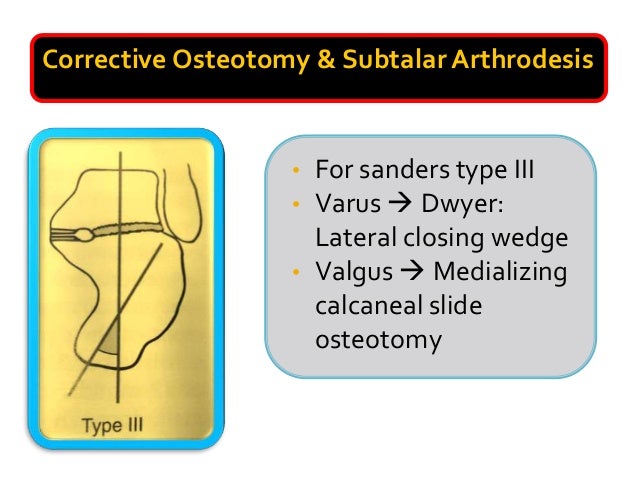
The calcaneal slide osteotomy is a common procedure used for the surgical correction of heel varus and valgus deformities.
If needed a laterally based wedge can be removed and or the osteotomy fragment can be translated cranially.
Most often surgical implants such as screws hold the bones together and support healing.
By extending the length of the calcaneus at the location of the talonavicular joint the talonavicular joint can be rotated from an abducted to neutral alignment.
The osteotomy is performed through an oscillating saw.
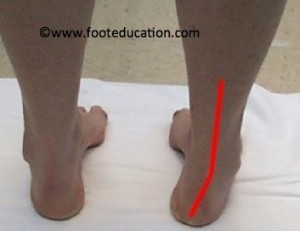
If perfectly aligned your heel bone should be directly underneath your shin bone tibia.
Methods and preliminary results.
A calcaneal osteotomy is a bone cut osteotomy that a surgeon makes across the heel bone calcaneus.
Then perform sharp dissection to the periosteal layer along the lateral aspect of the calcaneus.